By Senzeal | 29 October 2020 | 0 Comments
The Working Principle of CO2 Drop Checker
The Working Principle of CO2 Drop Checker
Since high-pressure CO2 was introduced to the aquatic plant industry 20 years ago, many people have tried to figure out how to measure CO2 concentration in water. There are so many kinds of CO2 monitors on the market that almost every aquarium related manufacturer will produce at least one type for sale. Does it help to maintain the ecological balance of fish tanks? Is it accurate? How does it work? The answers are as follows:
The instructions of a CO2 drop checker can be read:
1. Turn on the CO2 drop checker and add 2 to 3 drops of indicator;
2. Add water into the fish tank until reaching the waterline;
3. (Close the lid) Invert the checker until it is sucked on the place which is 10cm from the water surface;
There will also be a colorimetric scale of CO2 concentration. Actually, the working principle of the CO2 drop checker is related to chemical equilibrium, a comparison table, and an acid-base indicator.

1. Start with the simplest solution, BTB (Bromothymol Blue), which is an acid-base indicator
1) When the pH value is less than 6, the BTB gets H+ and turns yellow
2) When the pH value is greater than 7.6, the BTB loses H+ and becomes blue
3) When the pH value is equal to 7.1, the BTB shows green
2. CO2 is dissolved in water to form carbonic acid first, then the carbonic acid is dissociated to form bicarbonate radical and hydrogen ion. The reaction equilibrium equation is as follows: CO2(g)+H2O(l) →H2CO3(aq)→ HCO3-(aq)+H+(aq)
The three parts are not independent and are all reversible reactions. In addition to the concentration, they are also affected by temperature, pressure, and partial pressure of the gas in the space. In the equilibrium equation, (g) means gaseous, (l) means liquid, and (aq) means aqueous.
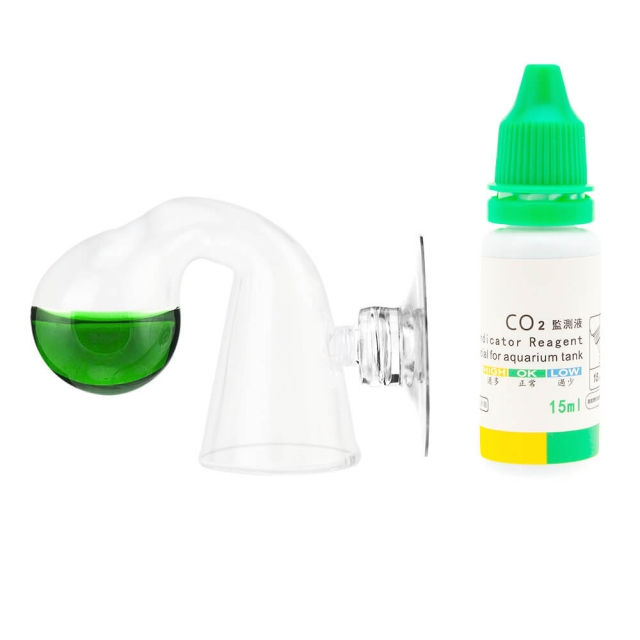
1) According to the equilibrium equation, the carbonic acid in the water will also become gaseous CO2 and escape into the air through the water surface. In the same way, it will enter the air chamber through the liquid level of the CO2 drop checker.
2) When the partial pressure of CO2 in the air chamber reaches the pressure of CO2 escaping from the water surface, the CO2 in the air chamber will dissolve into the reagent; Until the pressure of the tank water, the air chamber and the reagent is equal, there will be no CO2 escaping from the water surface of the CO2 drop checker, and at this time the pressure of them is equal to the partial pressure of the CO2 in the tank. According to the ideal-gas equation PV=nRT, the molecular weight (n can also be interpreted as concentration) is proportional to pressure and vice versa.

3) The CO2 dissolved into the reagent will perform the second half of the equilibrium equation. The CO2 will dissolve into water, and HCO3- and H+ will be dissociated. The pH value of the reagent is determined by the number of hydrogen ions, which changes the reagent color.
3. According to the comparison of the pH and KH in water with the colorimetric scale of CO2 concentration, the concentration of CO2 in the fish tank can be roughly measured.
Since high-pressure CO2 was introduced to the aquatic plant industry 20 years ago, many people have tried to figure out how to measure CO2 concentration in water. There are so many kinds of CO2 monitors on the market that almost every aquarium related manufacturer will produce at least one type for sale. Does it help to maintain the ecological balance of fish tanks? Is it accurate? How does it work? The answers are as follows:
The instructions of a CO2 drop checker can be read:
1. Turn on the CO2 drop checker and add 2 to 3 drops of indicator;
2. Add water into the fish tank until reaching the waterline;
3. (Close the lid) Invert the checker until it is sucked on the place which is 10cm from the water surface;
There will also be a colorimetric scale of CO2 concentration. Actually, the working principle of the CO2 drop checker is related to chemical equilibrium, a comparison table, and an acid-base indicator.

1. Start with the simplest solution, BTB (Bromothymol Blue), which is an acid-base indicator
1) When the pH value is less than 6, the BTB gets H+ and turns yellow
2) When the pH value is greater than 7.6, the BTB loses H+ and becomes blue
3) When the pH value is equal to 7.1, the BTB shows green
2. CO2 is dissolved in water to form carbonic acid first, then the carbonic acid is dissociated to form bicarbonate radical and hydrogen ion. The reaction equilibrium equation is as follows: CO2(g)+H2O(l) →H2CO3(aq)→ HCO3-(aq)+H+(aq)
The three parts are not independent and are all reversible reactions. In addition to the concentration, they are also affected by temperature, pressure, and partial pressure of the gas in the space. In the equilibrium equation, (g) means gaseous, (l) means liquid, and (aq) means aqueous.

1) According to the equilibrium equation, the carbonic acid in the water will also become gaseous CO2 and escape into the air through the water surface. In the same way, it will enter the air chamber through the liquid level of the CO2 drop checker.
2) When the partial pressure of CO2 in the air chamber reaches the pressure of CO2 escaping from the water surface, the CO2 in the air chamber will dissolve into the reagent; Until the pressure of the tank water, the air chamber and the reagent is equal, there will be no CO2 escaping from the water surface of the CO2 drop checker, and at this time the pressure of them is equal to the partial pressure of the CO2 in the tank. According to the ideal-gas equation PV=nRT, the molecular weight (n can also be interpreted as concentration) is proportional to pressure and vice versa.

3) The CO2 dissolved into the reagent will perform the second half of the equilibrium equation. The CO2 will dissolve into water, and HCO3- and H+ will be dissociated. The pH value of the reagent is determined by the number of hydrogen ions, which changes the reagent color.
3. According to the comparison of the pH and KH in water with the colorimetric scale of CO2 concentration, the concentration of CO2 in the fish tank can be roughly measured.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.Required fields are marked. *
CATEGORIES
- Aquarium Knowledge
- Aquarium Fishes
- Aquatic Plants
- Other Aquatic Creatures
- Best Aquarium Products
- Aquarium Light
- Aquarium Feeding Knowledge
- Fish Tank & Turtle Tank
- Aquarium Cleaning
- Fish Breeding
- Aquarium Heater
- Aquarium Filtration
- Planted Tank CO2
- Aquarium Decoration
- Shrimp Knowledge
- Aquascaping
- Algae
- Guppy
- Goldfish
- KOI
- Turtle
- Angelfish
- Betta
- Arowana
- Anemone
- Snails
- Fish Keeping
- Tropical
- CAT
- DOG
- BIRD